CH11、12 檔案系統實現、大量儲存系統 (File System 和 Mass-Storage Systems)
File System Implementation
Allocation Methods
- Contiguous allocation
- Linked allocation
- Indexed allocation
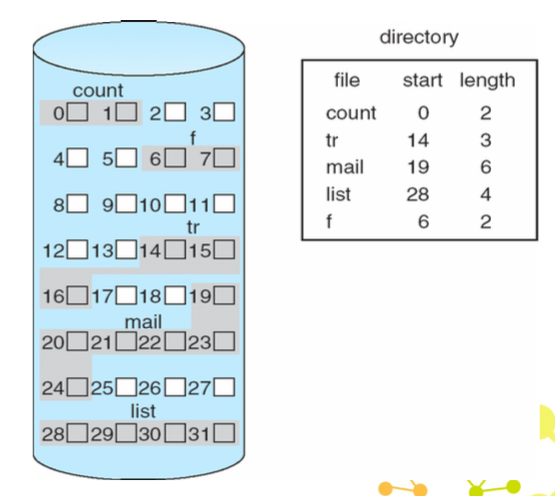
Contiguous allocation
- 優點:
- 簡單,只需要 start 和 length
- 缺點:
- external fragmentation
- files 不能再變大
Extent-Based Systems
為了解決 Contiguous allocation 的 external fragmentation 問題
- Contiguous + link 的做法
- 有 start,length,還有 pointer to next extent
- 缺點:
- 不能隨機 access,一定按照順序
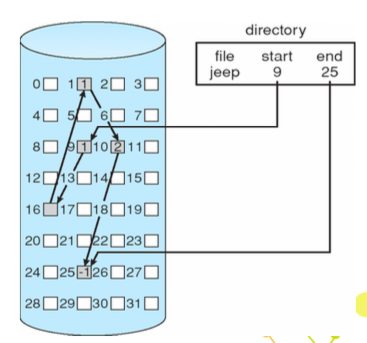
Linked allocation
全部用 link
- 優點:
- file 的大小不被限制
- 簡單,利用 start、end
- 資源使用率高,只要有空間就可以用,沒有 external fragmentation
- 缺點:
- 如果是 sequential access 那還可以,但 direct access 就會浪費,因為一直在搜尋前面的 pointer,重複搜尋
- 但是每個 block 裡面都要有 pointer,浪費空間
- Reliability,只要一個 pointer 不見了,整個壞掉了
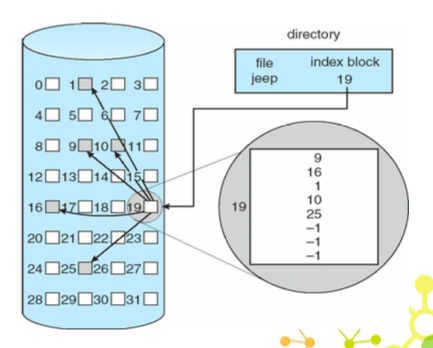
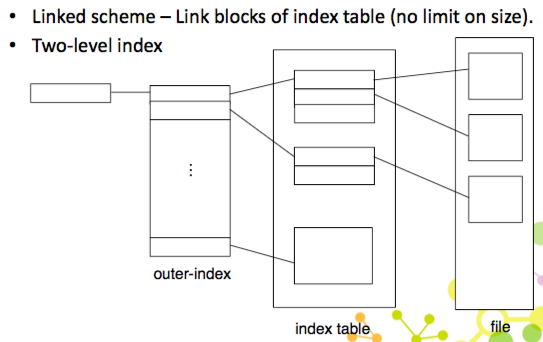
Indexed allocation
用一個 index block 存所有 pointer(以 array 的形式) 只要存 index block 就好
- 優點:
- direct access 一次就可以找到位置,sequential 也不會有問題
- 沒有 external fragmentation,只要空的就可以使用
- 缺點:
- 浪費空間,多一個 index block
- index block 可能會 internal fragmentation
- 如果 block 太多,可能會超過一個 index block 可以儲存的,就需要多個 index block 來存
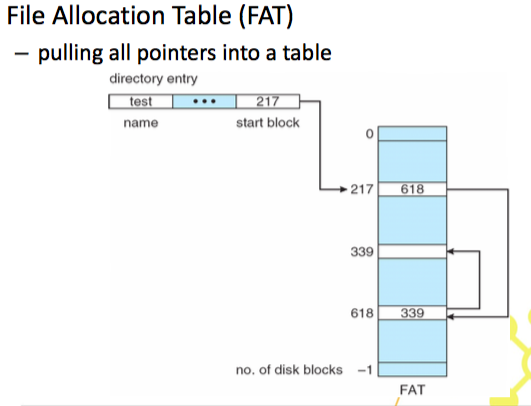
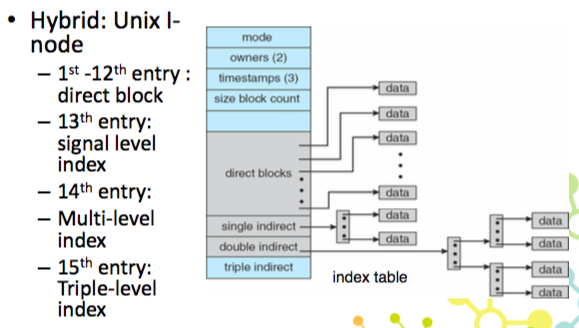
Indexed Allocation – Mapping
- Indexed + link
- hybrid
- 檔案很大就需要這種方式,但浪費空間
ch12 Mass-Storage Systems
Disk Scheduling
disk access time 分為
- seek time
- 移動磁頭 cylinder,往前往後
- rotational time
- 旋轉 disk 找到 sector
- read time
- tranfer time
降低 seek time 的排程
- Seektime 約= seekdistance
- First-come, first served (FCFS)
- Shortest-seek-time-first (SSTF)
- SCAN and C-SCAN
- LOOK and C-LOOK
FCFS
- 按照 track number 先來順序進行讀取
SSTF
- 移動到離最近的下一個距離
- 會有 starvation
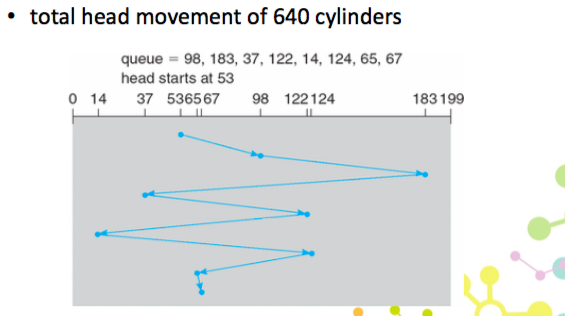
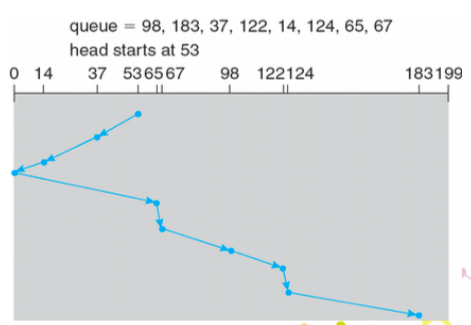
SCAN
- 先往一邊走,到底在往另一邊走
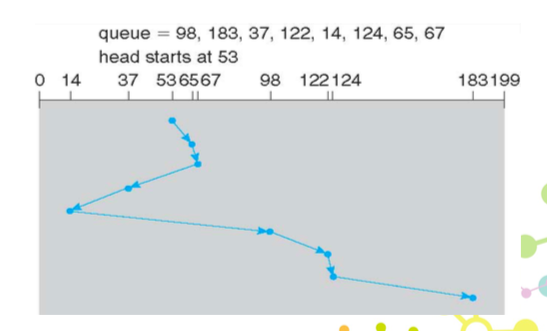
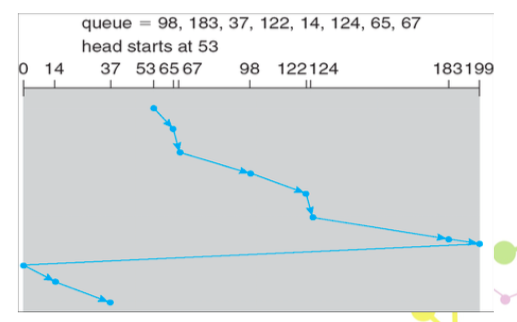
C-SCAN
- 為了要公平 等待時間
- 先往一邊走,走到底之後,直接移到另外一邊的底,從另外一邊的底開始走
C-LOOK
- look 不會走到底,會看 queue 裡最邊邊的
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.