CH9 虛擬記憶體管理 (Virtual-Memory Management)
- Virtual memory – separation of user logical memory from physical memory
- large process
- logical address space 可以大過 physical address space
- 增加 cpu/resources 使用率
- 簡單 programming
- More programs running concurrently
- faster
- Less I/O needed to load or swap processes
- large process
- Virtual memory 實現
- Demand paging
- Demand segmentation
demand paging
- 需要 page 才把他放進 memory
- Less I/O needed, no unnecessary I/O
- Faster response
- Less memory needed
- More users
- Less I/O needed, no unnecessary I/O
- Page is needed => reference to it
- invalid reference => abort
- not-in-memory => bring to memory
- Lazy swapper : never swaps a page into memory unless page will be needed
- Swapper 以 pages 為單位,不是以 process
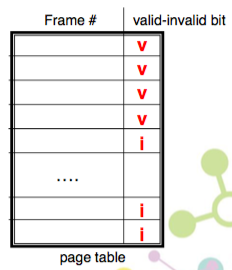
- 利用 Valid-Invalid Bit 知道到底有沒有用
- v : in-memory
- i : not-in-memory
- 如果是 bit 的值是 i 就叫做 page fault
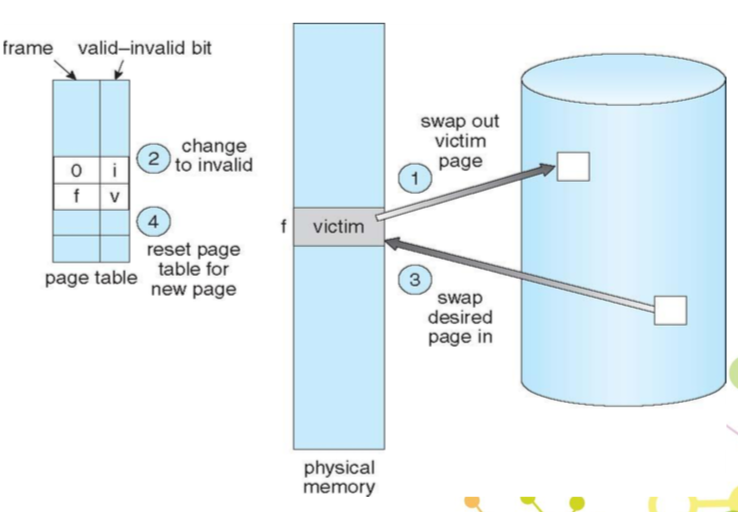
page fault
當有些 pages 不在 main memory 時
- 處理方式:
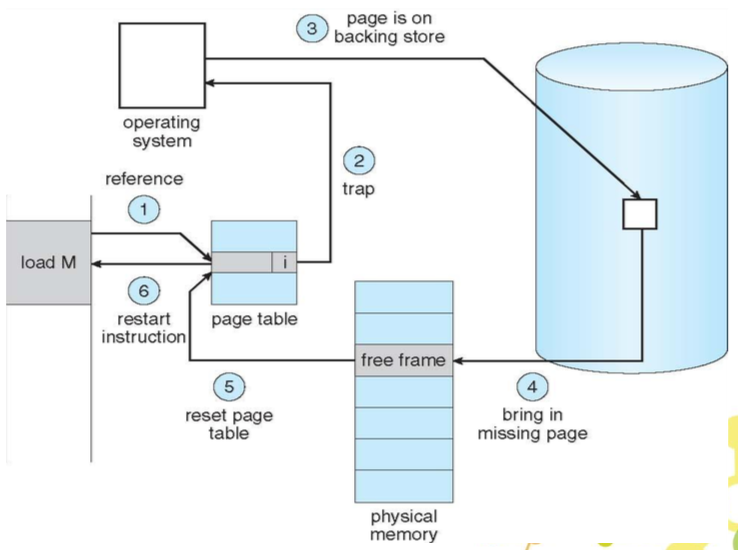
- 該 page 在 page table 的 Valid-Invalid Bit 為 invalid,發出 trap 給 os
- os 會去看另外一張 table(internal table)決定
- invalid reference => abort
- just not in memory => 繼續
- 找到空的 frame
- 將 page 從 disk swap in 進 memory
- reset table,把 validation bit 改為 v
- restart instruction
- Hardware support needed for demand paging
- Page table with valid / invalid bit
- Secondary memory (swap device with swap space)
- Instruction restart
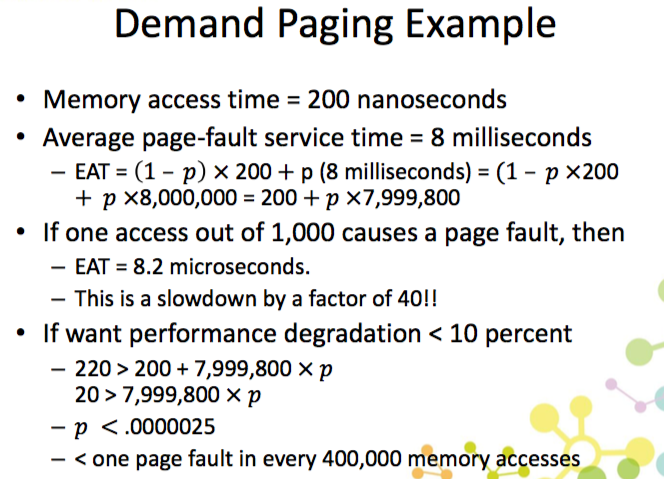
Performance of Demand Paging
- Page Fault Rate : 0<=p<1
- EAT = 1 – 𝑝 × memory access+ 𝑝 (page fault overhead+ swap page out+ swap page in+ restart overhead)
- 如何減少 PageFaultRate
- Page Replacement Algorithm
- Number of frame
- Page Size
- Program Structure
例題
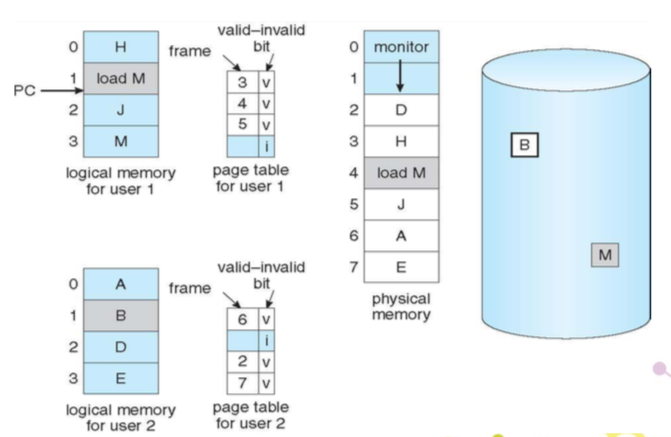
copy-on-write
我不記得老師有說耶..?
fork 時並不複製資料分頁,直到寫入時才複製
Page Replacement
- 當沒有 free frame 的時候,就要做 Page Replacement
- 把找一些沒用的 page swap out(踢出去)
- 檢查 modify bit
- modify(dirty) bit
- 在 memory 時有沒有被修改過
- 如果沒被修改過,可以直接被踢掉(因為 disk 本來就有一模一樣的)
- 處理方式:
- 找到造成 page fault 的 page 在 disk 的哪裡
- 找到空的 frame
- 如果是空的就直接使用
- 如果不是空的,就要 page replacement 演算法來挑選 victim frame
- 如果找到 dirty 的就踢掉他
- 將 page 從 disk swap in 進 memory
- reset table,把 validation bit 改為 v
- restart instruction
兩個問題
- frame-allocation algorithm
- 先每個 process 有多少 frame 可以用
- 哪些 frames 可以用
- Page-replacement algorithm
- 想要最低 page-fault rate on both first access and re-access
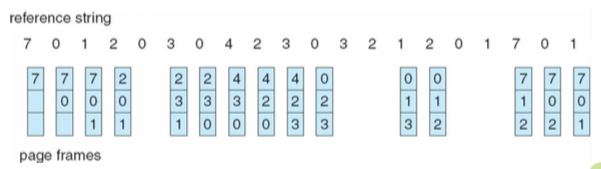
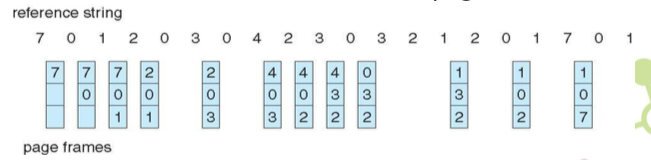
FIFO 演算法 (先來先被踢)
- 會發生 15 次 page faults
- page fault ratio = 15/20 = 75%
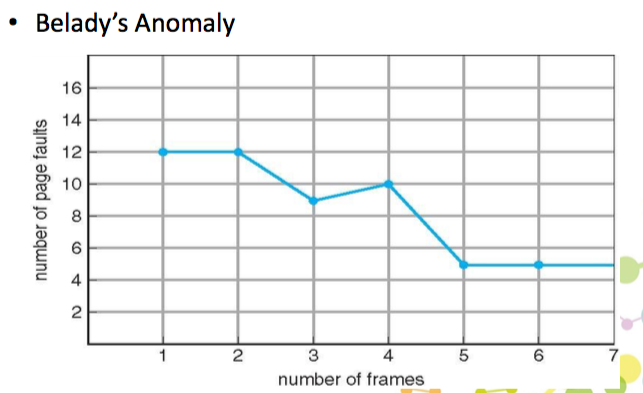
anomaly 奇怪的現象
當增加 frame 數量的話,原本以為 page fault 會減少,但事實上有可能會增加
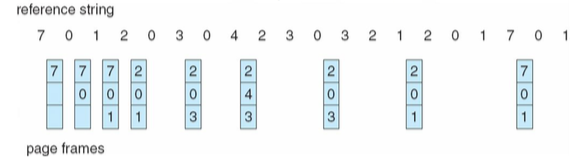
Optimal 演算法 (最晚被用到的先被踢)
- 會發生 9 次 page faults
- 但是有一個問題,你不能預知未來…
- 但但是我們可以拿其他的跟最佳做比較,知道哪個最接近
Least Recently Used (LRU) 演算法 (最久不被用到的先被踢)
- 會發生 12 次 page faults
- 比 FIFO 好,但比 optimal 差
- LRU and OPT 都是 stack algorithms,不會出現 Belady’s Anomaly
LRU 實現
由於很少電腦能夠提供足夠的硬體來支援真正的 LRU 頁替換,而 LRU 近似換頁法是一種以「參考位元」的方式來執行分頁替換的方法,利用參考位元來記錄過去使用過哪些分頁;雖然無法知道被使用的先後次序,但知道哪些被使用過而哪些還沒被使用。這種部分排班資訊可使許多分頁替換演算法盡量接近 LRU 替換法。
- counter implementation
- LFU Algorithm(count 最小,最少被使用就把它踢掉)
- MFU Algorithm(count 最大,最常被使用就把它踢掉)
- Search through table needed
- 比較貴
- 不太接近 opt
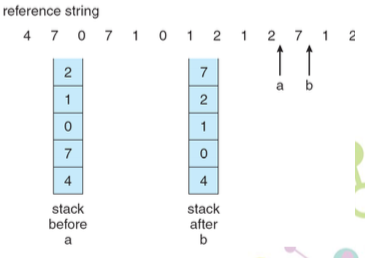
- stack implementation
LRU stack implementation
- 利用一個 reference bit 記錄
- 初始值為 0
- page 被 referenced 就設為 1
- Replace any with reference bit = 0 (if one exists)
- We do not know the order, however
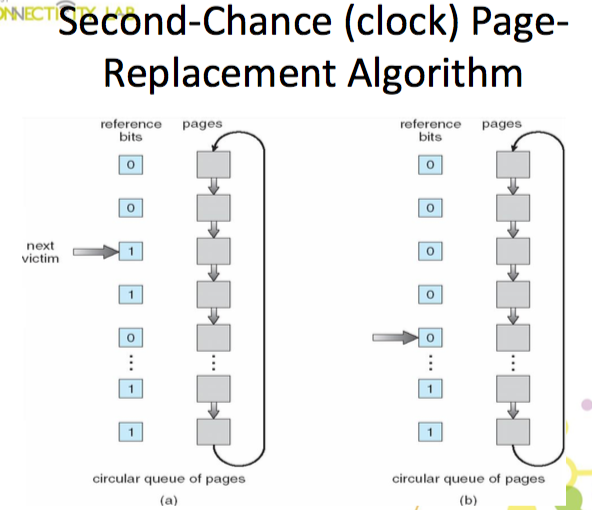
Second-chance algorithm
- 如果 reference bit = 0
- replace 他
- 如果 reference bit = 1
- 把他設為 0,但是把他留下來
- replace 下一個 page
Enhanced Second-Chance
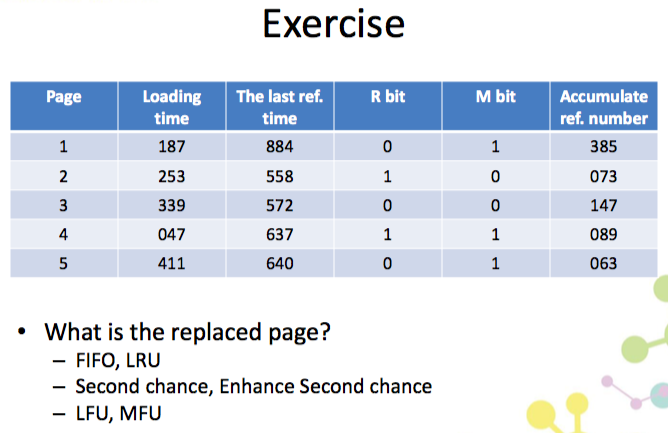
例題 (還沒寫喔!!!)
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.